Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
ATM
- Broadband ISDN (B-ISDN) is a set of communication protocols which are designed to transport a wide range of services simultaneously.
- The purpose of B-ISDN is to simplify and reduce the cost of communication between the interconnecting LAN's, multimedia conferencing, interactive games, image transmission etc.
- B-ISDN is the low-level MAC(Media Access control) protocol for transferring the actual data.
The ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) was designed with an aim to provide:
1. High speed data rate.
2. Low error rate between two or more switching centers.
3. Digital voice and videos.
4. Low operating cost.
Features of ATM
- Flexibility and versatility of voice, videos and images can be transmitted simultaneously over a single or integrated corporate network.
- Higher transmission capability.
- It provides support for virtual networks.
ATM Bit Rates
ATM supports four different types of bit rate:
1. Constant bit rate (CBR)- CBR traffic is derived from the source, where the information is transmitted at a constant rate. Example: Telephonic speech without silencer.
2. Variable Bit Rate (VBR)- Variable traffic is derived from a variable source. Example: Compressed voice or video with silence suppression.
3. Available Bit Rate (VBR)- When a carrier has allocated the necessary bandwidth on the links to carry CBR traffic and minimum VBR is guaranteed. The ABR is the mechanism to share the remaining bandwidth fairly between the links.
4. Unspecified Bit Rate (UBR)- In UBR, there is no guarantee about the bandwidth traffic delay and loss. The control of flow in UBR can be provided from the end device.
- The protocol which performs the operation of braking frames into the cells is known as ATM Adaptation Layer (AAL).
- Cells carrying speech and video must be received in the order they were sent. This is known as preserving data integrity and it is a function of ATM layer.
- Any link which preserves the order of data entering and leaving is known as channel.
- In ATM protocols, an end-to end connection is established before traffic and starts to flow. Then ,the traffic follows the same path through the network to achieve a true quality of service.
- The connection-less services are implemented with the help of AAL.
Architecture of ATM
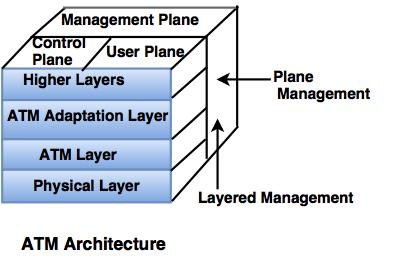 1. Physical layer
1. Physical layer- Physical layer is a point-to-point transfer mechanism at the top of hardware (it may be wire also).
- Physical layer adds its own information to each cell which is transmitted for link management.
Physical layer performs four functions:
i) Physical layer converts bits into cells.
ii) It transmits and receives the bits on physical medium.
Iii) Tracks the cell boundaries.
iv) Packaging of cell into frames.
ATM layer is common to all services which can have the packet transfer capabilities.
2. ATM layer- ATM layer provides the routing information to the data cells.
- ATM interfaces with the AAL and the Physical layer.
- Functions of ATM layer are under the network management, signaling and OAM protocol.
3. ATM Adaptation Layer- AAL provides the flexibility of a single communication process to carry the multiple types of traffic such as data, voice, video and multimedia.
- AAL is divided into two major parts.
- Upper part of the AAL is called as the convergence sublayer. Its task is to provide the interface to the application. The lower part of the AAL is called as the segmentation and reassembly (SAR) sublayer. It can add headers and trailers to the data units given to it by the convergence sublayer to form cell payloads.
