First C Program
Write down the following program in a text editor.Example: First C Program
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
printf(“\n Welcome to TutorialRide”);
}
Welcome to TutorialRide
In the above program
#include <stdio.h>- It is the preprocessor command. It is the first statement of the program.
- It starts with a hash (#) symbol.
- The #include will tell the compiler to include the standard input/output library file (stdio.h).
- The above file also has some built-in functions. By simply adding this file we can directly use the functions.
void main()
void will not return anything to the
main() function. If a parenthesis is not placed after the 'main', there will be a compilation error.
{ }- The curly brackets are used for grouping together all the statements.
- These statements together form the function body.
- They can be called as a set of instructions that are used for performing a given set of tasks.
printf(“\n Welcome to TutorialRide”);- The printf function is already defined in the stdio.h file.
- It is used for printing the text on the screen.
- Whatever message needs to be printed should be enclosed in double quotes inside brackets.
- '\n' is an escape character which represents a newline character.
Other escape characters are as follows:
| Escape Sequence | Purpose |
|---|
| \a | Audible signal |
| \b | It creates a backspace |
| \t | Tab |
| \n | Newline |
| \f | New page\Clear screen |
|
| \r | Carriage return |
| \? | Question mark |
| \\ | Back slash |
| \' | Single quote |
| \” | Double quote |
| \0 | Octal constant |
| \x | Hexadecimal constant |
Compilation and Execution of a C program
Every programming language has its own compiler.
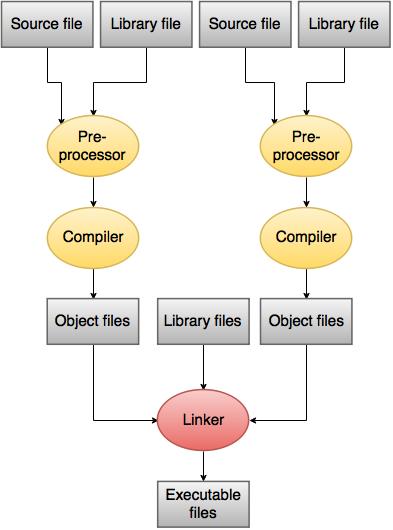
Process of compilation and execution:- The process starts with the source file and ends with the executable file.
- A source file is created which consists of statements written in C.
- The source file is then processed by the compiler.
- Compiler will translate the source code into object code. Object code contains the machine instructions for the CPU and calls the operating system API.
- The object file is not an executable file.
- The object file is then processed with a linker.
- There can be different compilers for the program but has a same linker for the object files.
- The output of this linker will be an executable file.
Following diagram explains us modular programming where the source code is divided into two or more source files . The source files are compiled separately which in turn produces multiple object files. These object files are combined by the linker for producing an executable file.