#include<iostream>
#include<math.h>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class area
{
float ar;
public:
area(float r)
{
ar=3.14*r*r;
}
area(float l, float b)
{
ar=l*b;
}
area(float a, float b, float c)
{
float s;
s=(a+b+c)/2;
ar=s*(s-a)*(s-b)*(s-c);
ar=pow(ar,0.5);
}
void display()
{
cout<<"\n Area : "<<ar;
}
};
int main()
{
int ch;
float x, y, z;
do
{
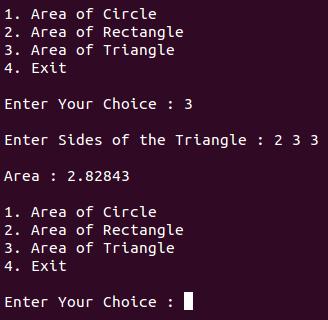
<<"\n\n 1. Area of Circle";
cout<<"\n 2. Area of Rectangle";
cout<<"\n 3. Area of Triangle";
cout<<"\n 4. Exit";
cout<<"\n\n Enter Your Choice : ";
cin>>ch;
switch(ch)
{
case 1 :
{
cout<<"\n Enter Radius of the Circle : ";
cin>>x;
area a1(x); //Class area, object is created : a1
a1.display();
}
break;
case 2 :
{
cout<<"\n Enter Length and Breadth of the Rectangle : ";
cin>>x>>y;
area a2(x,y);
a2.display();
}
break;
case 3 :
{
cout<<"\n Enter Sides of the Triangle : ";
cin>>x>>y>>z;
area a3(x,y,z);
a3.display();
}
break;
case 4 :
exit(0);
default :
cout<<"\n\n Invalid Choice ...";
}
} while(ch!=4);
return 0;
}