Introduction to arrays
- Array is a collection of variables of same type that stores the elements in the sequential manner.
- It is a data structure.
- Array elements consist of contiguous memory locations and are accessed randomly using the subscript or index variable.
- It stores a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type.
- In array, the lowest address corresponds to first element and highest address corresponds to the last element.
Declaring Arrays
- To declare an array, first specify the type of the elements and the number of elements required.
Syntax:
datatype arrayname [arraysize];
- The arraysize must be integer constant greater than 0.
Example:
int empid[5]; //We created array of 5 employees
- Array index starts from 0.
| Element | Description |
|---|
| empid[0] | It represents variable for 1st employee id. |
| empid[1] | It represents variable for 2st employee id. |
| empid[2] | It represents variable for 3st employee id. |
| empid[3] | It represents variable for 4st employee id. |
| empid[4] | It represents variable for 5st employee id. |
Initializing Arrays
Following are the three ways to initialize an Array:
1. Specify size and initialization will be done using the loop.
Example:
int empid[5];
for(i=0; i<5; i++)
cin>>empid[i];
2. Specify size and initialize array in a single statement.
Example:
empid[5]={101,102,103,104,105};
3. Without specifying size
Example:
empid[]={101,102,103,104,105};
The above example specifies the size of an array equal to 5.
Consider the following representation:

The above representation of an array is the pictorial form of an array, starts with 0.
Accessing Arrays
Example : Program demonstrating the declaring, initializing & accessing the arrays
#include<iostream>
#include <iomanip> //used for setw() function
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int a[ 5 ]; // a is an array of 5 integers
for ( int i = 0; i < 5; i++ ) // initialize elements of array
{
a[i] = i + 101; // set element at location i to i + 100
}
cout<<"Array Element"<<endl;
for ( int j = 0; j < 5; j++ ) //for displaying array element
{
cout<<setw(9)<<j<<setw(13)<<a[j]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
is used to format the output.
Output:
Array Element
0 101
1 102
2 103
3 104
4 105
Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- Multi-Dimensional Arrays are used to store data which requires multiple references.
Syntax:
data-type name [size1] [size2] . . . [size n];
- If we want to create Two-dimensional array then we can declare it as:int arr[3][3];
Where,
i. First dimension represents the number of rows.
ii. Second dimension represents the number of columns.
Consider the below representation of Two-dimensional array:
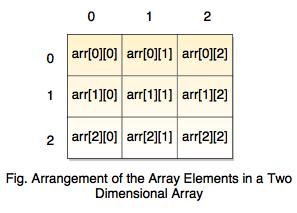
- The size of the array of the above figure is 3 X 3, but the indices will be from 0 to 2 in both rows and columns because array starts from 0.
- We can also have an array of more than two dimensions. Three-dimensional array has 3 dimensions, for example int a[2][2][2], but it is rarely used.
- Two-dimensional array has 2 dimensions. Matrix is the best example of two-dimensional array.
- It is the simplest form of multi-dimensional array.
- To initialize the two-dimensional arrays specify the bracketed values for each row.
For example:
int a[3][3] = {
{0,1,2}, //Initialize 0th row
{3,4,5}, //Initialize 1st row
{6,7,8} //Initialize 2nd row
};
- There is another way also to initialize the two-dimensional array:
int arr[3][2]={1,4,5,2,6,5}
Accessing Two-dimensional Arrays
Example : Program Demonstrating the Two-dimensional Arrays
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int arr[2][2] = {{0,0}, {1,2}}; //Two-dimensional array with 2 rows and 2 columns.
for ( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ ) //Output each array element's value
for ( int j = 0; j < 2; j++ )
{
cout<<"arr["<< i<<"]["<<j<<"]: ";
cout<<arr[i][j]<< endl;
}
return 0;
}
arr[0][0]: 0
arr[0][1]: 0
arr[1][0]: 1
arr[1][1]: 2
Passing arrays to the Function
Example: Demonstrating the passing arrays to the function
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
double getAverage(int marksarr[], int arrsize); // function declaration
int main ()
{
int marks[5] = {60,55,35,40,50}; // integer array with 5 elements.
double avg;
avg = getAverage(marks, 5); //passing array to the function as an argument.
cout <<"Average is: "<<avg<<endl;
return 0;
}
double getAverage(int marksarr[], int arrsize)
{
int i, sum = 0;
double avg;
for (i = 0; i < arrsize; ++i)
{
sum += marksarr[i];
}
avg = double(sum) / arrsize;
return avg;
}
Average is: 48

