interface stackop
{
void push(int item);
int pop();
}
class FixedStack implements stackop
{
private int stk[ ];
private int tos;
FixedStack(int size)
{
stk=new int[size];
tos=-1;
}
public void push(int item)
{
if(tos==stk.length-1)
{
System.out.println("Stack Overflows");
int t[ ]=new int[stk.length * 2];
for(int i=0;i<stk.length;i++)
t[i]=stk[i];
stk=t;
stk[++tos]=item;
}
else
stk[++tos]=item;
}
public int pop()
{
if(tos<0)
{
System.out.println("Stack Underflows");
return 0;
}
else
return stk[tos--];
}
}
class DynStack implements stackop
{
private int stk[ ];
private int tos;
DynStack(int size)
{
stk=new int[size];
tos=-1;
}
public void push(int item)
{
if(tos==stk.length-1)
{
System.out.println("Stack Overflows.");
int t[ ]=new int[stk.length * 2];
for(int i=0;i<stk.length;i++)
t[i]=stk[i];
stk=t;
stk[++tos]=item;
}
else
stk[++tos]=item;
}
public int pop()
{
if(tos<0)
{
System.out.println("Stack Underflows.");
return 0;
}
else
return stk[tos--];
}
}
class StackTest
{
public static void main(String args[ ])
{
FixedStack fs=new FixedStack(3);
DynStack ds=new DynStack(5);
stackop mystk;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
fs.push(i);
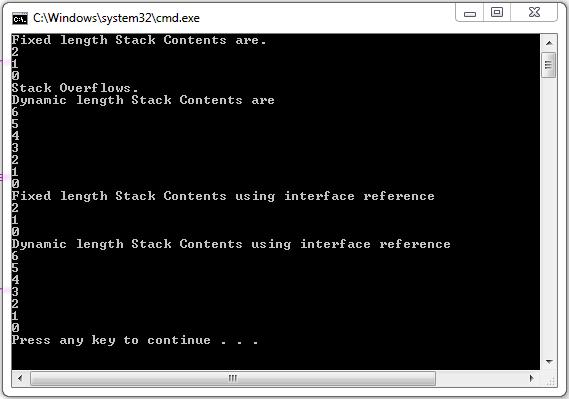
System.out.println("Fixed length Stack Contents are.");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
System.out.println(fs.pop());
for(int i=0;i<7;i++)
ds.push(i);
System.out.println("Dynamic length Stack Contents are");
for(int i=0;i<7;i++)
System.out.println(ds.pop());
mystk=fs;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
mystk.push(i);
System.out.println("Fixed length Stack Contents using interface reference");
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
System.out.println(mystk.pop());
mystk=ds;
for(int i=0;i<7;i++)
mystk.push(i);
System.out.println("Dynamic length Stack Contents using interface reference");
for(int i=0;i<7;i++)
System.out.println(mystk.pop());
}
}