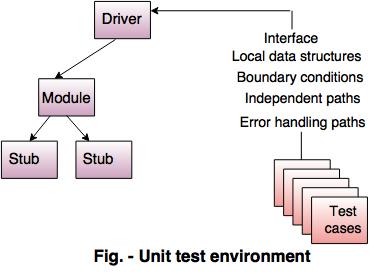
| Stub | Driver |
|---|
| Stub is considered as subprogram. | It is a simple main program. |
| Stub does not accept test case data. | Driver accepts test case data. |
| It replace the modules of the program into subprograms and are tested by the next driver. | Pass the data to the tested components and print the returned result. |
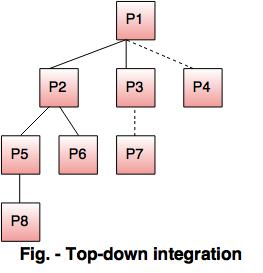
a. Top-down integration
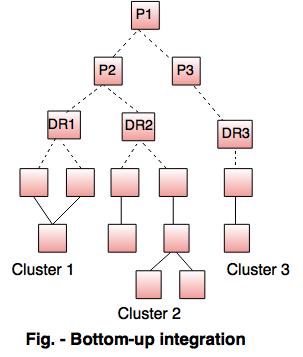
b. Bottom-up integration
In bottom up integration testing the components are combined from the lowest level in the program structure.
| Regression testing | Smoke testing |
|---|
| Regression testing is used to check defects generated to other modules by making the changes in existing programs. | At the time of developing a software product smoke testing is used. |
| In regression tested components are tested again to verify the errors. | It permit the software development team to test projects on a regular basis. |
| Regression testing needs extra manpower because the cost of the project increases. | Smoke testing does not need an extra manpower because it does not affect the cost of project. |
| Testers conduct the regression testing. | Developer conducts smoke testing just before releasing the product. |
| Alpha testing | Beta testing |
|---|
| Alpha testing is executed at developers end by the customer. | Beta testing is executed at end-user sites in the absence of a developer. |
| It handles the software project and applications. | It usually handles software product. |
| It is not open to market and the public. | It is always open to the market and the public. |
| Alpha testing does not have any different name. | Beta testing is also known as the field testing. |
| Alpha testing is not able to test the errors because the developer does not known the type of user. | In beta testing, the developer corrects the errors as users report the problems. |
| In alpha testing, developer modifies the codes before release the software without user feedback. | In beta testing, developer modifies the code after getting the feedback from user. |