#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define MAX 10 // Macro defines maximum no. of elements in the list. It is a user defined data type
struct
{
int list[MAX];
int element; //new element to be inserted
int pos; //position of the element to be inserted or deleted
int length; //total no of elements
}l;
enum boolean
{
true, false
};
typedef enum boolean boolean; //function prototypes
int menu(void); //This function displays the list of operations
void create(void); //This function creates initial set of elements
void insert(int, int); //This function inserts the element at specified position
void delet(int); //This function deletes the element at given position
void find(int); //This function finds the position of the given element, if exists
void display(void); //This function displays the elements in the list
boolean islistfull(void); //This function checks whether the list is full or not boolean
boolean islistempty(void); //This function checks whether the list is empty or not
void main()
{
int ch;
int element;
int pos;
l.length = 0;
while(1)
{
ch = menu();
switch (ch)
{
case 1: l.length = 0;
create();
break;
case 2:
if (islistfull() != true)
{
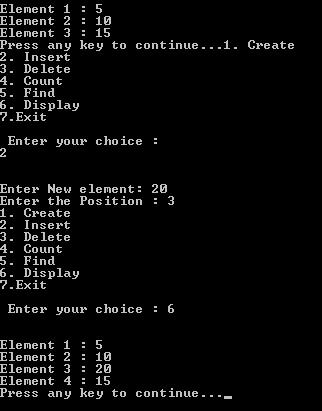
printf("Enter New element: ");
scanf("%d", &element);
printf("Enter the Position : ");
scanf("%d", &pos);
insert(element, pos);
}
else
{
printf("List is Full. Cannot insert the element");
printf("\n Press any key to continue...");
getch();
}
break;
case 3:
if (islistempty() != true)
{
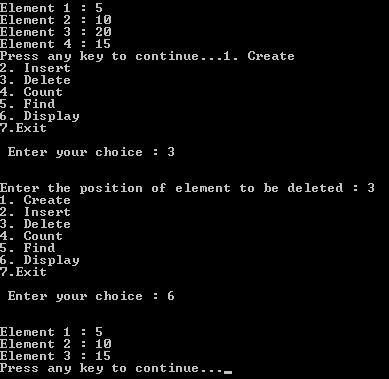
printf("Enter the position of element to be deleted : ");
scanf("%d", &pos);
delet(pos);
}
else
{
printf("List is Empty.");
printf("\n Press any key to continue...");
getch();
}
break;
case 4:
printf("No of elements in the list is %d", l.length);
printf("\n Press any key to continue...");
getch();
break;
case 5:
printf("Enter the element to be searched : ");
scanf("%d", &element);
find(element);
break;
case 6:
display();
break;
case 7:
printf("Exit");
exit(0);
break;
default: printf("Invalid Choice");
printf("\n Press any key to continue...");
getch();
}
}
} //function to display the list of elements
int menu()
{
int ch;
//clrscr();
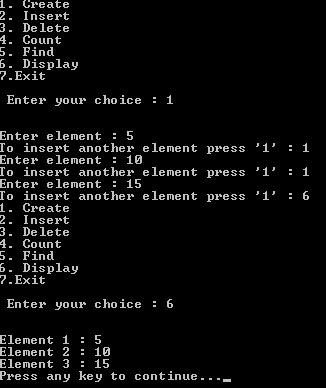
printf("1. Create\n2. Insert\n3. Delete\n4. Count\n5. Find\n6. Display\n7.Exit\n\n Enter your choice : ");
scanf("%d", &ch);
printf("\n\n");
return ch;
}
void create(void)
{
int element;
int flag=1;
while(flag==1)
{
printf("Enter element : ");
scanf("%d", &element);
l.list[l.length] = element;
l.length++;
printf("To insert another element press '1' : ");
scanf("%d", &flag);
}
}
void display(void)
{
int i;
for (i=0; i<l.length; i++)
printf("Element %d : %d \n", i+1, l.list[i]);
printf("Press any key to continue...");
getch();
}
void insert(int element, int pos)
{
int i;
if (pos == 0)
{
printf("\nCannot insert an element at 0th position")
getch();
return;
}
if (pos-1 > l.length)
{
printf("\nOnly %d elements exit. Cannot insert at %d position", l.length, pos);
printf("\n Press any key to continue...");
getch();
}
else
{
for (i=l.length; i>=pos-1; i--)
{
l.list[i+1] = l.list[i];
}
l.list[pos-1] = element;
l.length++;
}
}
void delet(int pos)
{
int i;
if(pos == 0)
{
printf("\nCannot delete at an element 0th position");
getch();
return;
}
if (pos > l.length)
{
printf("\n\n Only %d elements exit. Cannot delete", l.length, pos);
printf("\n Press any key to continue...");
getch();
return;
}
for (i=pos-1; i<l.length; i++)
{
l.list[i] = l.list[i+1];
}
l.length--;
}
void find(int element)
{
int i;
int flag = 1;
for (i=0; i<l.length; i++)
{
if(l.list[i] == element)
{
printf ("%d exists at %d position",element, i+1);
flag = 0;
printf("\n Press any key to continue...");
getch();
break;
}
}
if(flag == 1)
{
printf("Element not found.\n Press any key to continue...");
getch();
}
}
boolean islistfull(void)
{
if (l.length == MAX)
return true;
else
return false;
}
boolean islistempty(void)
{
if (l.length == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
| Array | Linked List |
|---|---|
| Array is a collection of elements having same data type with common name. | Linked list is an ordered collection of elements which are connected by links. |
| Elements can be accessed randomly. | Elements cannot be accessed randomly. It can be accessed only sequentially. |
| Array elements can be stored in consecutive manner in memory. | Linked list elements can be stored at any available place as address of node is stored in previous node. |
| Insert and delete operation takes more time in array. | Insert and delete operation cannot take more time. It performs operation in fast and in easy way. |
| Memory is allocated at compile time. | Memory is allocated at run time. |
| It can be single dimensional, two dimensional or multidimensional. | It can be singly, doubly or circular linked list. |
| Each array element is independent and does not have a connection with previous element or with its location. | Location or address of element is stored in the link part of previous element or node. |
| Array elements cannot be added, deleted once it is declared. | The nodes in the linked list can be added and deleted from the list. |
| In array, elements can be modified easily by identifying the index value. | In linked list, modifying the node is a complex process. |
| Pointer cannot be used in array. So, it does not require extra space in memory for pointer. | Pointers are used in linked list. Elements are maintained using pointers or links. So, it requires extra memory space for pointers. |